volume lv | lv volume echo volume lv Learn how to calculate left ventricular mass and volume using ultrasound formulas and RW. Find a Store Near You. Product details. Delivery & Returns. Gifting. OnTheGo MM. $3,100.00. Item Unavailable. LOUIS VUITTON Official USA site - Discover our latest OnTheGo MM, available exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton stores.
0 · normal lv volume
1 · lv volume echo
2 · lv systolic volume normal range
3 · lv systolic volume
4 · lv stroke volume normal range
5 · lv stroke volume
6 · lv end systolic volume
7 · lv diastolic volume normal range
Rapid decrease of blood pressure does not alter the regional dynamics of the left ventricle during exercise in patients without coronary artery disease, but it may induce normalization, worsening, or changes in the site of wall motion abnormalities in hypertensives with significant coronary stenoses. © 1997 American Journal of .
Find normal values for aorta, atria, ventricles, valves and pulmonary veins in 2D echocardiography. Compare mild, moderate and severe regurgitation and stenosis of mitral and tricuspid valves.
Learn how to calculate left ventricular mass and volume using ultrasound formulas and RW.
This review article covers various echocardiographic methods to assess LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE). STE can .Find normal values for aorta, atria, ventricles, valves and pulmonary veins in 2D echocardiography. Compare mild, moderate and severe regurgitation and stenosis of mitral and tricuspid valves.This review article covers various echocardiographic methods to assess LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE). STE can detect subclinical LV dysfunction and predict cardiac outcomes for different cardiac and noncardiac conditions.
End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the left ventricle before the heart contracts. It affects stroke volume, cardiac output, and heart function. Learn how it is measured and what.Learn how to calculate left ventricular mass and volume using ultrasound formulas and RWT (Relative Weight Thickness). Find out how to diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy based on wall thickness and mass.Learn how to measure and calculate the left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV) using the Teicholz formula or the spherical formula. Find out the optimal view, the correction factor and the factors that affect the accuracy of the volume analysis. Learn how to extend your root or home directory filesystem partition using Logical Volume Manager (LVM) in Linux. Follow the steps to create, identify, and extend a Physical Volume, Volume Group, and Logical Volume with lvextend command.
normal lv volume
Learn how to measure LV size and function using 2DE or 3DE methods, and compare normal values for ejection fraction, strain, and regional wall motion. This document also covers RV size and function assessment and common pitfalls in chamber quantification.Learn how to generate and interpret left ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops from cardiac cycle diagrams. Understand the factors that affect the slope and area of the PV loop, such as ventricular compliance, preload, afterload and inotropy. Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain. Find out how strain analysis can improve diagnosis and management of heart failure, valvular disease, and cardiotoxicity.
lv volume echo
Learn how to assess left ventricular systolic function using echocardiography, including linear, area, and volume measurements. Find out the normal values and pathological changes of LV internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs) and other parameters.Find normal values for aorta, atria, ventricles, valves and pulmonary veins in 2D echocardiography. Compare mild, moderate and severe regurgitation and stenosis of mitral and tricuspid valves.
This review article covers various echocardiographic methods to assess LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE). STE can detect subclinical LV dysfunction and predict cardiac outcomes for different cardiac and noncardiac conditions. End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the left ventricle before the heart contracts. It affects stroke volume, cardiac output, and heart function. Learn how it is measured and what.
Learn how to calculate left ventricular mass and volume using ultrasound formulas and RWT (Relative Weight Thickness). Find out how to diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy based on wall thickness and mass.Learn how to measure and calculate the left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV) using the Teicholz formula or the spherical formula. Find out the optimal view, the correction factor and the factors that affect the accuracy of the volume analysis. Learn how to extend your root or home directory filesystem partition using Logical Volume Manager (LVM) in Linux. Follow the steps to create, identify, and extend a Physical Volume, Volume Group, and Logical Volume with lvextend command.
Learn how to measure LV size and function using 2DE or 3DE methods, and compare normal values for ejection fraction, strain, and regional wall motion. This document also covers RV size and function assessment and common pitfalls in chamber quantification.Learn how to generate and interpret left ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops from cardiac cycle diagrams. Understand the factors that affect the slope and area of the PV loop, such as ventricular compliance, preload, afterload and inotropy. Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain. Find out how strain analysis can improve diagnosis and management of heart failure, valvular disease, and cardiotoxicity.

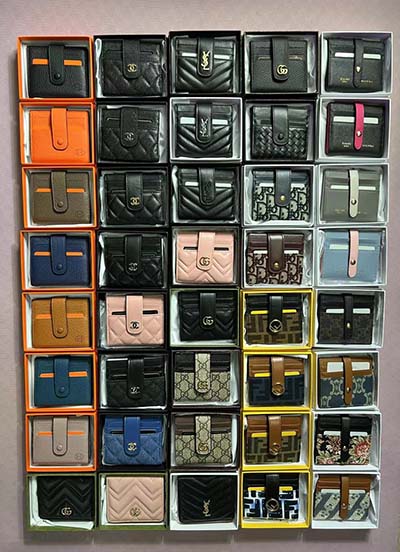
chanel snapback for cheap
lv systolic volume normal range
101 007 runā par šo
volume lv|lv volume echo