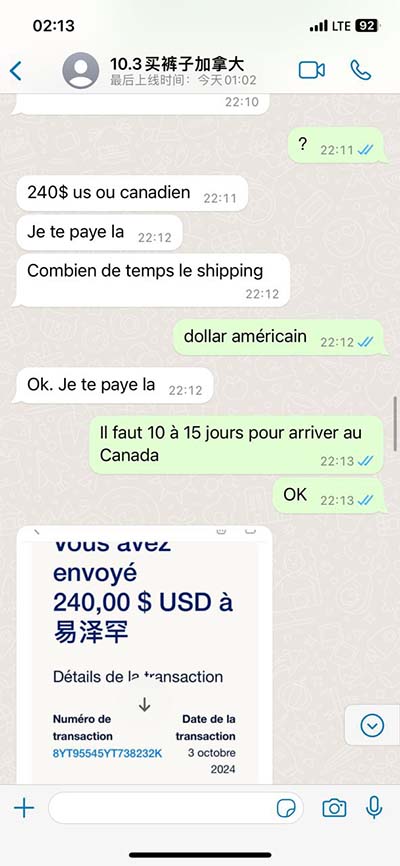
lv dilation mitral regurgitation | mitral regurgitation volume lv dilation mitral regurgitation Decompensated MR is characterized by substantial and progressive LV dilation, elevated LV diastolic pressure, increased systolic wall stress, and an EF <50%. The decline in EF is a consequence of depressed myocardial contractile state, LV afterload excess, or both. 40 mi. .
0 · mitral valve regurgitation video
1 · mitral regurgitation volume
2 · mitral regurgitation ratio chart
3 · mitral regurgitation left ventricular response
4 · mitral regurgitation and dilatation
5 · mitral regurgitation
6 · mild mitral valve regurgitation
7 · lv response to mitral regurgitation
Choreographer by Sugeng (INA)&Rita (INA) -Mei 2024 Count 32 Wall 4 6 Tag no restart level high beginner Dance by Diamond Lita LD#litalinedance #linedanceclas.
Decompensated MR is characterized by substantial and progressive LV dilation, elevated LV diastolic pressure, increased systolic wall stress, and an EF <50%. The decline in EF is a consequence of depressed myocardial contractile state, LV afterload excess, or both.PK 6 Woa«, mimetypeapplication/epub+zipPK 6 W .
Establishment of the role of pathways that lead to heritable hypercoagulable .The dynamics of acute mitral regurgitation were studied in six open-chest dogs in . Mitral regurgitation is a heart condition characterized by the incomplete closure of the mitral valve, leading to the backflow of blood from . Decompensated MR is characterized by substantial and progressive LV dilation, elevated LV diastolic pressure, increased systolic wall stress, and an EF <50%. The decline in EF is a consequence of depressed myocardial contractile state, LV afterload excess, or both.
Mitral valve regurgitation is the most common type of heart valve disease. In this condition, the valve between the left heart chambers doesn't close fully. Blood leaks backward across the valve. If the leakage is severe, not enough blood moves through the heart or to the rest of the body. Mitral regurgitation is a heart condition characterized by the incomplete closure of the mitral valve, leading to the backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium during systole. This results in a systolic murmur heard at the .
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is incompetency of the mitral valve causing flow from the left ventricle (LV) into the left atrium during ventricular systole. MR can be primary (common causes are mitral valve prolapse and rheumatic fever) or secondary to LV dilation or infarction.Untreated severe mitral valve regurgitation (MR) will eventually lead to left ventricular (LV) dilatation followed by LV dysfunction and onset of symptoms. The optimal time of surgery would be before the decompensated stage where irreversible damage to the left ventricle can occur.Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a complex valve lesion that can pose significant management challenges. This expert consensus decision pathway emphasizes that recognition of MR should prompt an assessment of its etiology, mechanism, and severity, as well as consideration of the indications for treatment. Mitral valve insufficiency or mitral regurgitation (MR) is characterized by the reversal of blood flow from the left ventricle (LV) to the left atrium (LA), typically in the systolic phase of the cardiac cycle. It continues to be a significant issue in .
Mitral regurgitation (MR), which is also known as mitral insufficiency, is a common heart valve disorder. When MR is present, blood leaks backwards through the mitral valve when the heart contracts. This reduces the amount of blood that is pumped out to the body.Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a complex valve lesion that can pose significant management challenges for the cardiovascular clinician. This Expert Consensus Document emphasizes that recognition of MR should prompt an assessment of its etiology, mechanism, and severity, as well as indications for treatment.
Surgical mitral valve repair is the gold-standard treatment in severe primary (mainly degenerative) mitral regurgitation, with excellent durability and restoration of normal life. Decompensated MR is characterized by substantial and progressive LV dilation, elevated LV diastolic pressure, increased systolic wall stress, and an EF <50%. The decline in EF is a consequence of depressed myocardial contractile state, LV afterload excess, or both.Mitral valve regurgitation is the most common type of heart valve disease. In this condition, the valve between the left heart chambers doesn't close fully. Blood leaks backward across the valve. If the leakage is severe, not enough blood moves through the heart or to the rest of the body.
Mitral regurgitation is a heart condition characterized by the incomplete closure of the mitral valve, leading to the backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium during systole. This results in a systolic murmur heard at the .
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is incompetency of the mitral valve causing flow from the left ventricle (LV) into the left atrium during ventricular systole. MR can be primary (common causes are mitral valve prolapse and rheumatic fever) or secondary to LV dilation or infarction.Untreated severe mitral valve regurgitation (MR) will eventually lead to left ventricular (LV) dilatation followed by LV dysfunction and onset of symptoms. The optimal time of surgery would be before the decompensated stage where irreversible damage to the left ventricle can occur.Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a complex valve lesion that can pose significant management challenges. This expert consensus decision pathway emphasizes that recognition of MR should prompt an assessment of its etiology, mechanism, and severity, as well as consideration of the indications for treatment.
Mitral valve insufficiency or mitral regurgitation (MR) is characterized by the reversal of blood flow from the left ventricle (LV) to the left atrium (LA), typically in the systolic phase of the cardiac cycle. It continues to be a significant issue in . Mitral regurgitation (MR), which is also known as mitral insufficiency, is a common heart valve disorder. When MR is present, blood leaks backwards through the mitral valve when the heart contracts. This reduces the amount of blood that is pumped out to the body.Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a complex valve lesion that can pose significant management challenges for the cardiovascular clinician. This Expert Consensus Document emphasizes that recognition of MR should prompt an assessment of its etiology, mechanism, and severity, as well as indications for treatment.
mitral valve regurgitation video
michael kors kids canada
The aim of this documentation is to outline the FAT procedure of Low Voltage Main Switchboard. A) Visual Inspection Test B) Insulation Test C) High Voltage Injection Test D) Primary Current Injection Test E) Metering Current Transformer Polarity Test F) Secondary Current Injection Test 1.2 Working Location Approved LV main switchboard to be .
lv dilation mitral regurgitation|mitral regurgitation volume